pipe() Source Driver
The pipe source driver opens a named pipe with the specified name and listens for messages. It is used as the native message delivery protocol on HP-UX.
Important Information
Pipe is very similar to the file() driver, but there are a few differences, for example, pipe() opens its argument in read-write mode, therefore it is not recommended to be used on special files like /proc/kmsg. In fact, it is not recommended to use pipe() on anything else than real pipes.
Status
| Architecture | Status |
|---|---|
| x86 | Works |
| ARM | Works |
How to Test
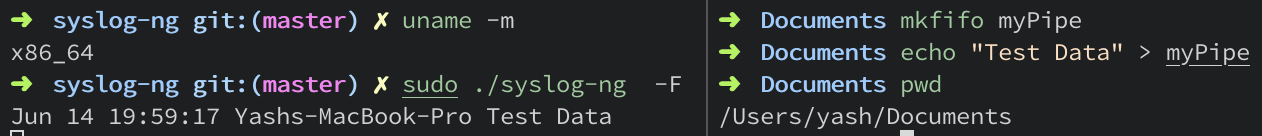
To test the pipe() source driver, we can create a pipe using the mkfifo command. The mkfifo command basically lets you create FIFOs (a.k.a named pipes). Following is the syntax of the command:
mkfifo [OPTION]... NAME...
Configuration File Used
@version: 3.31
@include "scl.conf"
source s_pipe {
pipe("/Users/yash/Documents/myPipe");
};
destination console{
file(/dev/stdout);
};
log {
source(s_pipe);
destination(console);
};
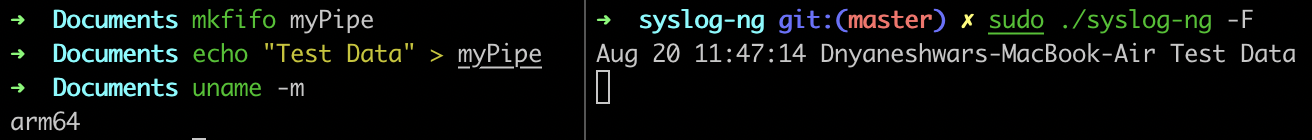
Proof