redis
The Redis module has only one driver, which is the Redis() destination driver. The Redis() driver sends messages as name-value pairs to a Redis key-value store.
Status
| Architecture | Status |
|---|---|
| x86 | Works |
| ARM | Works |
Testing
Redis Setup
To test this driver, we need to set up a Redis store first. You can use Homebrew to brew install all the necessary dependencies.
To be able to successfully test this driver, we need to install Redis and libHIREDIS. To install all these, we need to do the following:
$ brew install redis
$ brew install hiredis
To run Redis in the background, use:
$ brew services start redis
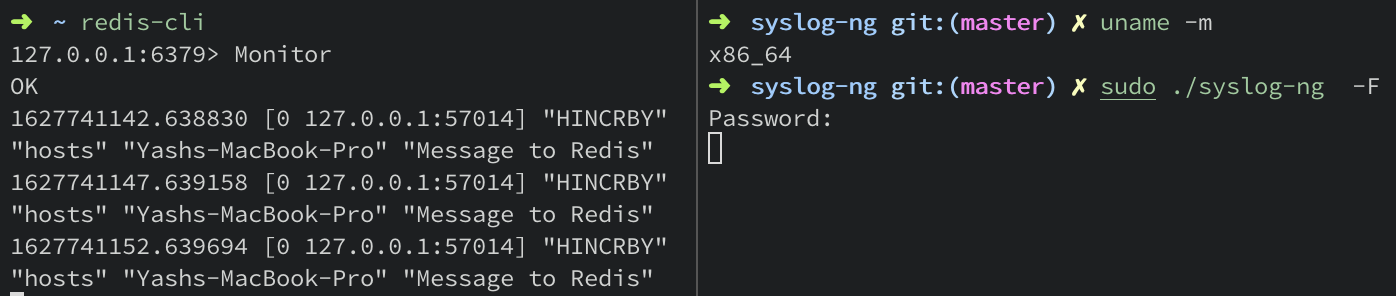
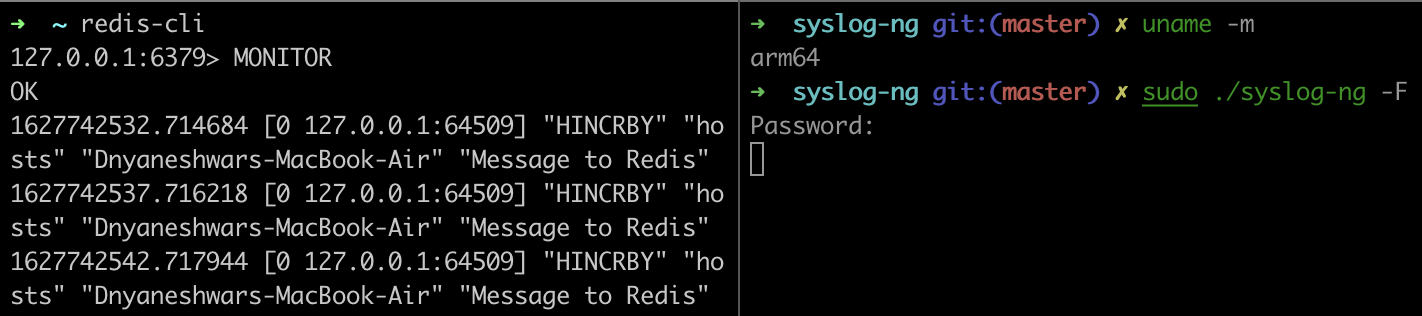
Once we do this, we can use the Redis CLI to monitor for messages that we will send using syslog-ng. To do this, use the monitor command on Redis CLI.\
$ redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> MONITOR
Note: Localhost on port 6379 is the default setting for redis.
Configuration File Used
@version: 3.33
@include "scl.conf"
options {
stats-freq(10);
time-reopen(10);
};
source custom
{
example-msg-generator(
num(20)
freq(5)
template("Message to Redis")
);
};
destination d_redis {
redis(
host("localhost")
port(6379)
command("HINCRBY", "hosts", "${HOST}", "${MESSAGE}")
);
};
log {
source(custom);
destination(d_redis);
};
Proof