python-fetcher() Source Driver
The python-fetcher() source allows you to write your own source in Python. You can import external Python modules to receive or fetch the messages.
Important Information
-
Fetcher-style sources that actively fetch messages. In general, write fetcher-style sources (for example, when using simple blocking APIs), unless you explicitly need a server-style source.\
-
The Python block must be a top-level block in the syslog-ng OSE configuration file.\
-
If you store the Python code in a separate Python file and only include it in the syslog-ng OSE configuration file, make sure that the PYTHON_PATH environment variable includes the path to the Python file, and export the PYTHON_PATH environment variable.
Python sources consist of two parts. The first is a syslog-ng OSE source object that you define in your syslog-ng OSE configuration and use in the log path. This object references a Python class, which is the second part of the Python source. The Python class receives or fetches the log messages, and can do virtually anything that you can code in Python. You can either embed the Python class into your syslog-ng OSE configuration file, or store it in an external Python file. For this test, we will embed the Python class into the configuration file.
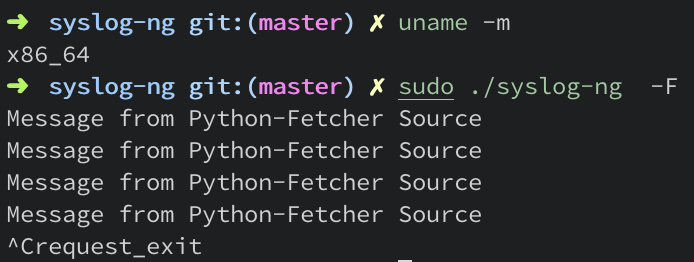
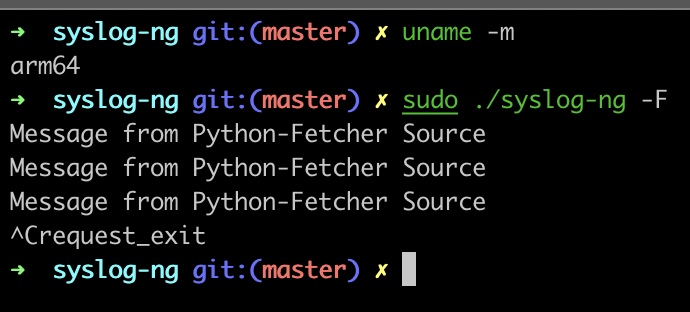
Status
| Architecture | Status |
|---|---|
| x86 | Works |
| ARM | Works |
Configuration File Used
@version: 3.33
@include "scl.conf"
destination console{
file(/dev/stdout);
};
source s_python{
python-fetcher(
class("TestPython")
);
};
python {
from syslogng import LogFetcher
from syslogng import LogMessage
class TestPython(LogFetcher):
def fetch(self): # mandatory
# return LogFetcher.FETCH_ERROR,
# return LogFetcher.FETCH_NOT_CONNECTED,
# return LogFetcher.FETCH_TRY_AGAIN,
# return LogFetcher.FETCH_NO_DATA,
return (LogFetcher.FETCH_SUCCESS, "Message from Python-Fetcher Source")
def request_exit(self):
print("request_exit")
# If your fetching method is blocking, do something to break it
# For example, if it reads a socket: socket.shutdown()
};
log {
source(s_python);
destination(console);
};
Proof